The study prepared by Analytical Credit Rating Agency (ACRA) analyzed the financial stability of regions of Far Eastern Federal District.
The Roscongress Foundation presents the salient points of the publication accompanied by fragments of broadcasts of relevant panel discussions from the business programme of international events held by the Roscongress Foundation.
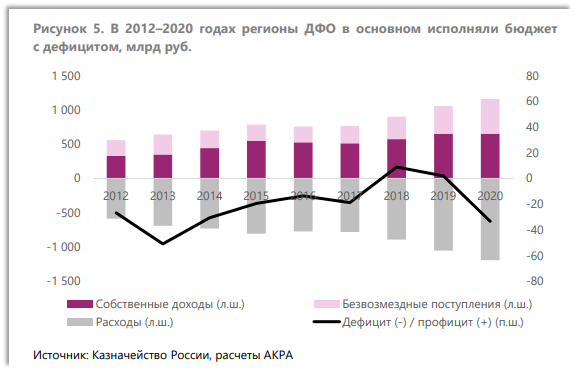
Regions of Far Eastern Federal District have deficits in their budgets.
Regions in Far Eastern Federal District have deficits in their budgets due to various factors. For instance, the study notes that the need to cover budget deficits in regions of Far Eastern Federal District leads to an increase in their debt burden and a reduction of their account balances. The study explains the high level of current expenditures and the limited scope for increasing revenues by the fact that, over the last nine years, the aggregate budget performance of the regions under consideration has been positive on only two occasions. And only three regions of Far Eastern Federal District ended the four-year period from 2016 to 2020 with a combined surplus: Chukotka Autonomous District, Amur Region, and Primorye Territory. The regions with the largest budget deficits over the same period were Khabarovsk Territory, the Republic of Buryatia, Sakhalin Region, Jewish Autonomous Region, and Kamchatka Territory.
Among other factors that contribute to the deficit nature of this district budget, the authors cite low liquidity, as well as low flexibility of the expenditure side of budgets. For example, only Sakhalin Region, has placed surplus funds in bank deposits every year since 2016, which has generated additional income for the region. Also, it was in Sakhalin Region, as well as in Chukotka Autonomous District, that the average share of capital expenditure exceeded the national average among all Far Eastern regions during the same period. These facts illustrate low liquidity and budget flexibility.
An important factor influencing the deficit nature of Far Eastern Federal District budgets is also the mismatch between area and population density, which leads to a higher per capita fiscal spending requirement than the Russian average. Thus, six of the ten largest Russian regions by area and four of the five with the smallest total population are located in this district. However, there are also significant differences in gross regional product (GRP) per capita between the regions of the district, both between themselves and compared to the Russian average for regions that do not specialize in mineral extraction. This limits their ability to form the budget revenue base.
The debt burden between the regions of the district is unevenly distributed.
It is worth noting that over the past five years, the public debt of the regions of Far Eastern Federal District has increased in absolute terms to 35.9 billion rubles. Bank loans predominate in its structure, followed by budget loans and bonds, with government guarantees making up the rest. According to the study, the debt burden as well as the debt structure is unevenly distributed. At the beginning of 2021, the following regions had the highest debt burden: Jewish Autonomous Region, Zabaikalye Territory and Khabarovsk Territory. The rest of the district regions did not exceed 50% of tax and non-tax revenues (NTRs). The lowest debt indicators were found in Primorye Territory and Sakhalin Region.
The district is increasingly dependent on transfers from the federal budget.
The share of own revenues (NTRs) has been markedly lower than the national average over the last five years a trend characteristic of the other federal districts as well, which show a decline in the number of NTRs in revenues. This trend in 2020 was due to additional funding from the federal budget to support the regions during the coronavirus infection and the implementation of preventing measures within restrictions imposed.
But it is important to note that while the overall share of own revenues in Russia fell by 12%, in Far Eastern Federal District it fell by 14%. The study also notes that the increase of NTRs in the Far Easter Federal District budget is not only due to the pandemic. For example, Sakhalin Region stands out among all the regions of the district: it is the only Far Eastern region that does not receive subsidies for fiscal capacity equalization, and its share of own revenues exceeds the national level. It is noted that the figure for fiscal capacity equalization grants is higher in the district than the national average 37% for Far Eastern Federal District and 19% nationally.
It is worth noting that Kamchatka is characterized by the lowest share of its own revenues among the regions of the district, while Yakutia receives the largest amount of uncompensated revenues in absolute terms.
The authors conclude that investment in development of regions of Far Eastern Federal District will be the main driver for increasing their financial sustainability in the future.
For more information, see the special sections of the Roscongress Foundation Information and Analytical System: StayHomeEconomy, dedicated to possible ways to stabilize the economy during the pandemic; Financial market and Investment projects, which are devoted to issues of investment and the financial sector; as well as Far East, which contains materials about development of this region.






