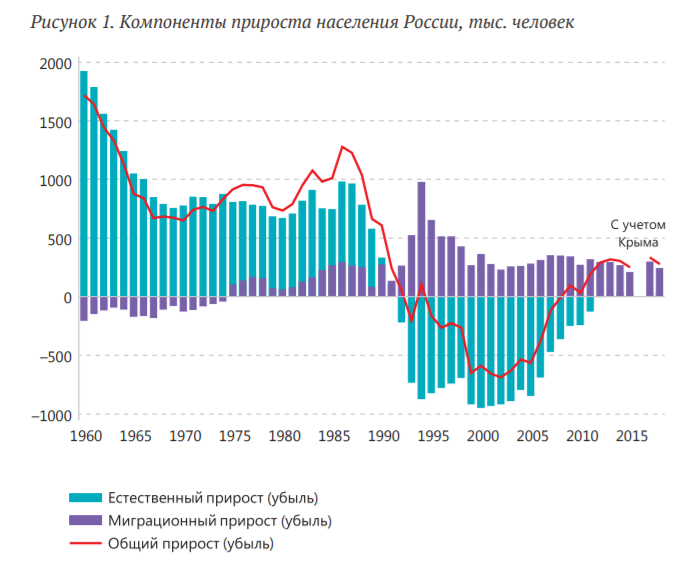
Demographic challenges create serious problems, since they require a substantial «reconfiguration» of many social and economic institutions, cultural and legal norms and practices that have developed in the past and historically adapted to those demographic realities that no longer exist.
An example is the irreversible changes in the age structure, the so-called «demographic aging». A new age structure is no worse and no better than the previous one, but it is different and will never be the same as it has been recently.
This fundamental demographic shift puts almost all life support systems in new conditions: the labour market and consumer market, education system and healthcare, pension system and leisure system. This list is not exhaustive. Adaptation to new conditions is a challenge that all countries are trying to address with varying success, and Russia is no exception.
But in Russia, the acuteness of this challenge is exacerbated by a number of historical and even geographical circumstances, sometimes rooted in a distant, and sometimes in a very recent past. The most obvious of these circumstances are social and military upheavals of the first half of the 20th century.
They destabilised demographic processes, deformed a sex and age pyramid of the population in the country and thus gave rise to long-term consequences for the demographic development of Russia, which have not been eliminated to date.
To be sure, a social policy both in the post-war USSR and in post-Soviet Russia largely ignored both the opportunities created by the demographic transition and challenges it generates, which also adversely affects the present demographic situation in the country, and its demographic prospects.
Thus, demographic challenges facing Russia include challenges generated by evolutionary processes common to all countries and perturbation factors existed in the last century of Russia.
The report outlines 7 groups of such challenges:
• underpopulation;
• demographic changes;
• low fertility rates;
• high mortality;
• internal migration;
• immigration;
• emigration.
In conclusion, some considerations are given regarding the ways of responding to these challenges and social measures necessary for their implementation.
However, the authors of the report are aware that their ability to discuss such measures is limited. These measures should be comprehensive and cover diverse spheres of society. Development of such measures involves bringing together a very wide range of experts, including experts with different specialties.