In this publication, the Analytical Credit Rating Agency (ACRA) studies prospective changes in the Bank of Russias monetary policy in 2020. Analysts consider such factors as the possibility of reducing the key rate, monetary policies of the central banks of developing countries, etc. According to ACRA, the tightness of monetary policy is based on the previous assessment of pro-inflationary risks arising from the introduction of restrictions, financial stability risks, and the timing of the onset of the coronavirus epidemic in Russia. Choosing the key rates minimum value will depend on how significant a threat to inflation expectations the Bank of Russia considers lifting self-isolation restrictions to be compared to the threat of weak demand.
The Roscongress Foundation presents the salient points of the publication accompanied by fragments of broadcasts of relevant panel discussions from the business programme of international events held by the Roscongress Foundation.
The Bank of Russia has considered and will continue to consider the possibility of reducing the key rate by 1 percentage point.
Back in April, the vast majority of analysts did not consider such a significant easing as a baseline scenario, as evidenced by both consensus forecasts and market indicators. The main question posed by ACRA is this: will the signal about room for monetary policy easing mean a significant reduction in the key rate in the coming months?
Moreover, in the initial phase of the crisis, expectations were rather revised towards an increase in the key rate, as evidenced by both market indicators and the consensus forecasts of economists.
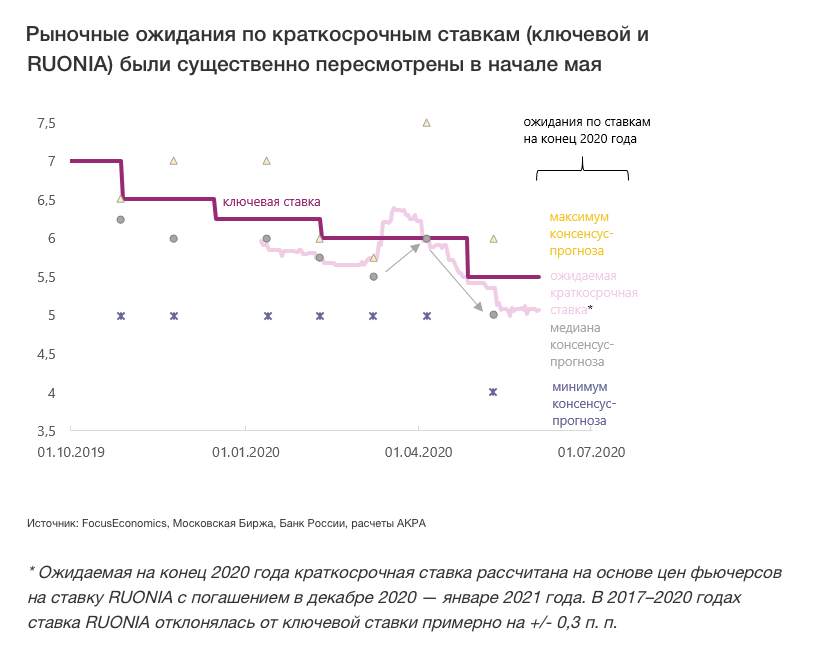
In particular, according to a FocusEconomics survey from April 5, 2020, none of the representatives of investment banks, rating agencies, or expert organizations (21 respondents) publicly expected a reduction in the key rate to less than 5% by the end of 2020 in the baseline scenario, and on average expectations were close to 6%. However, on May 10, after lowering the rate by 0.5 percentage points and the re-emergence of information about the decision options discussed by the Board of Directors of the Bank of Russia, expectations were revised down by an average of almost 0.5 percentage points.
Even reducing the key rate by 1 percentage point would not allow the Bank of Russia to match the degree of monetary policy softness demonstrated by the central banks of most developing countries that also adhere to an inflation-targeting regime.
Russias key rate at 5.5% is still close to the so-called neutral rate, which in a recession can be considered evidence of a relatively tight interest rate policy. Based on the real external parity model, ACRA estimates the neutral rate for Russia at 5.56% in 2020, which is lower than the Bank of Russias public target of 67%.
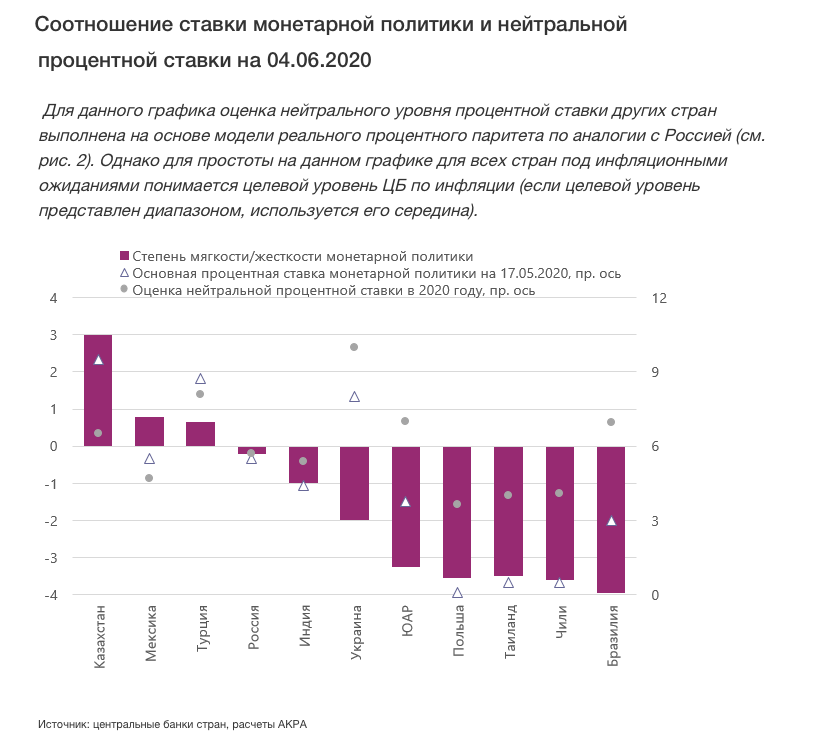
The reasons for the significant difference in the degree of softness or tightness in the monetary policies of developing countries lie in a significantly different set and balance of factors taken into account by the central banks when determining the level of the key rate. In particular, the differences are due to the heterogeneity of fiscal policies and the different levels of stability in banking systems. Now, it seems that the beginning of the coronavirus epidemic in each individual country happening at different times is playing a particularly important role.
Choosing the key rates minimum value within 45.5% will depend on how significant a threat to inflation expectations the Bank of Russia considers lifting self-isolation restrictions in mid-summer to be compared to the threat of weak demand.
Taking the above into account, ACRA is maintaining the long-term key rate expectations expressed in its baseline macroeconomic forecast: 5.5% in 2022 and a lowering to 55.25% by 2024. However, analysts consider it very likely that in 2020 key rate decisions will be driven by the need to provide stimulus to a larger extent than was previously expected. In particular, the June meeting of the Bank of Russia will probably result in a rate cut of 0.250.75 percentage points, and the rate established as a result of these summer cut (or cuts, should more follow) will be left unchanged until at least Q2 2021. Data on consumer demand after the lifting of quarantine measures, the possibility of re-imposing these measures, and unemployment figures for MayJune will be of vital importance to the Central Bank at its summer key rate meetings.
In ACRAs opinion, growth of the key rate must be retained in the pessimistic macroeconomic forecast given the risks of financial stability, which logically arise from the negative prerequisites of this scenario.
For more information about possible ways to stabilize the economy during a pandemic, please see theStayHomeEconomy special section of the Roscongress information and analytical system, and the Financial market and Monetary policy sections about various aspects of monetary policy and financial market development opportunities.






