The study by ACRA is focused on the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on economic indicators and the relationship between the pace of vaccination and economic recovery.
The Roscongress Foundation presents the salient points of the publication accompanied by fragments of broadcasts of relevant panel discussions from the business programme of international events held by the Roscongress Foundation.
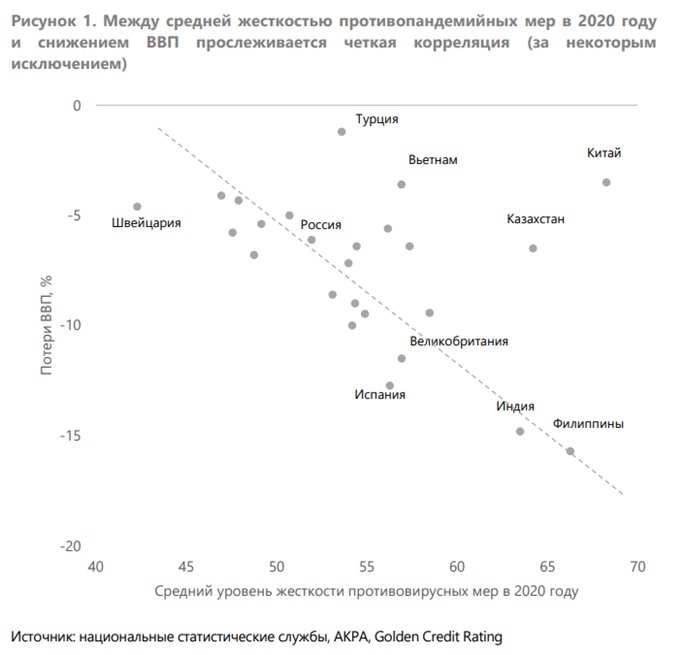
The overall GDP loss strongly correlated with the strictness of counter-pandemic measures.
This is true for the majority of countries, which together represent 81% of global GDP and 62% of the worlds population, bar some exceptions. Overall GDP loss strongly correlated with the strictness of the counter-pandemic measures. On average, lockdowns and restrictive measures resulted in 7.1 pp of GDP contraction, with variations depending on countries economic structures and the severity of quarantine measures. This impact was mainly felt as a result of self-isolation regimes. Also, lower demand for consumer goods and services led to an output contraction among goods producers and service providers. However, there were some exceptions. Despite having comparably high severity of quarantine measures, four countries China, Turkey, Vietnam and Kazakhstan suffered much less economic losses than others, while Switzerland underwent a larger contraction.
The authors of the report note that the majority of countries imposed quarantine measures in a coordinated manner. Coronavirus-related restrictions were in place during almost all of 2020 in major economies. During the first wave of the pandemic, April was the month with the strictest quarantine measures in most of the countries.
Video: https://roscongress.org/sessions/sleduyushchie-20-let/search/#02:23:19.960
Among the most affected sectors were transport, construction, mining, and services.
On average, the most affected industries in 2020 compared to 2019 turned out to be transport (-10.7%), construction (-7.4%), mining (-7.4%), and services (-7.7%). Less affected were retail and manufacturing, which rebounded to a varying extent during the second half of 2020.
By summarizing available statistics the authors of the report identified a number of structural features which could have pushed countries potential economic losses caused by the COVID-19 pandemic above the average: higher than average dependence on external tourism; inadequate capacity of healthcare facilities or uneven access to medical services; elevated share of investment-oriented goods produced within a countrys manufacturing sector; historically low share of online business in retail trade and financial services. In some cases, potential losses were mitigated by successful policies, fortunate economic or export structure, or less political willingness to curb the pandemic.
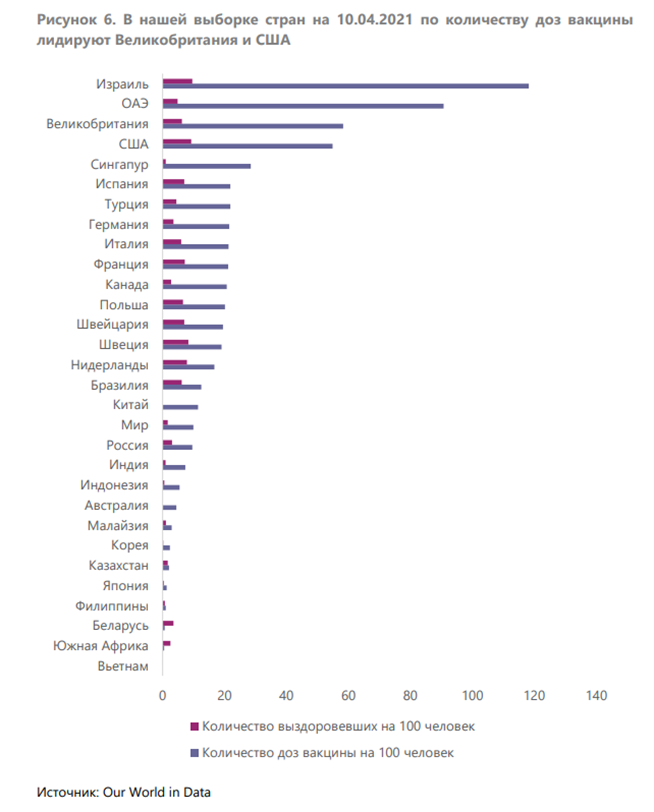
Vaccination programs are likely to be implemented in an uneven manner and with harmful implications for the economies.
The vaccination process, which was launched in many countries at the onset of 2021, is not yet widespread enough to talk about the end of pandemic globally. The absolute frontrunners are Israel and the United Arab Emirates, where 118 and 91 doses per 100 people respectively have been administered as of April 10, 2021. The United Kingdom and United States had managed to narrow the gap with the frontrunners with 58 doses and 55 doses per 100 people, respectively. The gap between the leaders and the average is primarily due to the speed of vaccination, which depends on peoples trust in the vaccine(s) available in their countries, the size of population, and sufficiency of doses. However, the average for the whole world is 10 doses per 100 people, which is far from sufficient to ensure the end of recurring lockdowns. The different pace of vaccination globally may delay the formation of herd immunity in some countries, making future economic recovery and budget consolidation highly uneven.
For more information about global challenges and responses to them, see the Sustainable Development and Economic Inequality sections of the Roscongress Information and Analytical System, and the StayHomeEconomy and COVID-19 sections about possible ways to stabilize the economy during the pandemic.






