Research by Accenture, an ecosystem-based IT consulting firm, uncovers additional potential for companies to reduce their carbon footprint by leveraging cloud-based data services.
The Roscongress Foundation presents the salient points of the publication accompanied by fragments of broadcasts of relevant panel discussions from the business programme of international events held by the Roscongress Foundation.
The use of cloud storage is turning from a welcome addition to a must for companies, and the expansion of data centers increases energy consumption.
The use of cloud storage and the phenomenon of «cloud migration» itself is becoming ubiquitous. The proliferation of data centers and the transfer of IT infrastructure to cloud services reduces company costs and brings benefits to shareholders and all participants in the process. Accenture estimates that migrating to the cloud reduces the total cost of ownership (storage costs) by 30-40%, which offers advantages for companies compared to storing data on their own infrastructure.
The number of data centers is increasing by 14% every year, and the cost of cloud services in 2020 increased by 17% compared to the previous year. According to some experts, American IT companies spend about 11.4% of their costs on cloud services. In China, this indicator is at 2.7%, but this gap is rapidly decreasing.
However, despite all the advantages of cloud storage, the price of it is increased energy consumption. Global electricity consumption by data centers is already equivalent to the annual consumption of a country like Spain.
Taking a greener approach, cloud migration could reduce CO2 emissions by 59 million tonnes annually, or 5.9% of the IT industrys emissions.
Such a reduction in emissions, according to the authors of the study, is equivalent to the emissions of 22 million cars. At the same time, such an ambitious reduction could pave the way for even greater commitments to reduce the carbon footprint of big data businesses.
This can be achieved by following a series of sequential steps. First of all, it is necessary to take a responsible approach to the choice of a cloud service provider, assessing the level of their commitment to sustainable development. In this regard, the energy source for the centers is especially important (whether it is renewable) as well as the degree of optimization of processes. Potentially sustainable cloud migration can reduce CO2 emissions by over 84% compared to conventional storage infrastructure. For such a reduction, it is necessary to increase the energy efficiency of data centers, including cooling systems, the efficiency of equipment and computing resources, and so on.
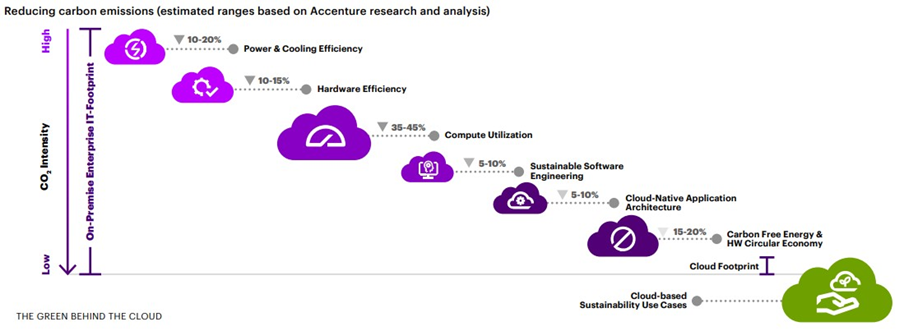
Accenture experts identify three levels of action to help reduce your carbon footprint through cloud migration: bronze, silver and gold.
The «bronze» level implies a simple «cloud migration», which, thanks to the more efficient data centers, will reduce energy consumption by 65% and CO2 emissions by 84%.
The «silver» level requires a more sustainable approach to software. The choice of programming language, for example, affects the level of energy consumption.
As an illustrative example, the authors cite the training of artificial intelligence to distinguish between types of colors: increasing the selection accuracy from 96 to 96% leads to a sevenfold increase in power consumption. That is why the «gold» level requires optimization of software for the needs of cloud storage systems (cloud-native). This requires customization of computing processes depending on the «demand» for data (on-demand computing) and dynamic resource allocation.
For more information, see the special sections of the Roscongress Foundation Information and Analytical System:Digitalization, Environment, IT industry, dedicated to how digital solutions can contribute to environmental protection and decarbonization.





