The study prepared by WTO experts examines recent trends in world trade. The review analyzed statistics on the coronavirus impact on trade, identified key trends and prospects for the global market.
The Roscongress Foundation presents the salient points of the publication accompanied by fragments of broadcasts of relevant panel discussions from the business programme of international events held by the Roscongress Foundation.
In 2020, trade in goods and services fell sharply due to the coronavirus pandemic and related restrictions.
In 2020, the coronavirus pandemic led to an 8% drop in goods trade and a 21% year-on-year reduction in commercial services trade. Thus, global exports of produced goods fell by 5.2% in 2020, while total merchandise exports fell by 7.7% overall.
The study shows, that the impact of COVID-19-related restrictions on trade in goods and services varies: services are much more severely affected. Thus, trade in services fell by 30% in 2Q 2020, compared with a 23% drop for goods over the same period. While restrictions led to the cancellation of flights, vacations abroad, restaurant meals and cultural/entertainment events, demand for basic necessities persisted in all major economies. Unlike goods, services cannot be stockpiled, which means that large revenue losses are likely to persist.
The study notes that the travel and transport industries were the hardest hit in the services sector. Thus, international travel expenses decreased by 81% and transport costs by 29% in Q2 2020. The decline in transport was similar to that during the 2009 financial crisis. However, unlike in 2009, the decline in transport services was mainly due to restrictions on passenger traffic and a drop in demand for international transport, rather than a sharp decline in freight traffic.
Other services sectors were unevenly affected. Thus, sectors that require physical labor of people at close range, such as construction, as well as personal, cultural and recreational services, have declined sharply. In contrast, financial services continued to grow.

It is worth noting that trade in health products increased by 16.3 per cent in 2020, compared with an increase of 4.7 per cent in 2019, when the pandemic first started: trade in personal protective equipment increased the most (+47.2 per cent).
Despite minor improvements, most regions and countries around the world have seen trade rates fall in 2020 because of the pandemic.
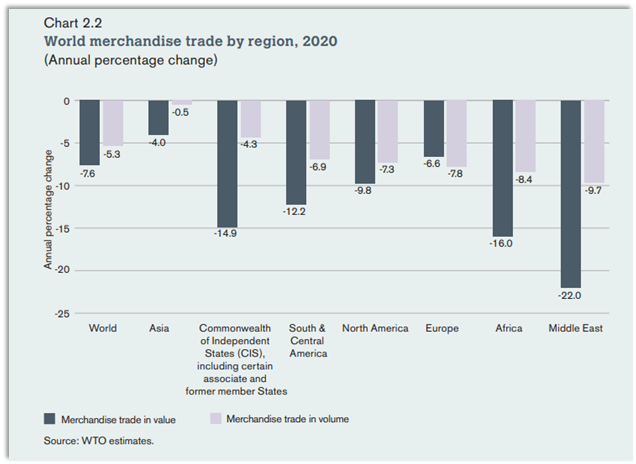
All regions recorded a decline in trade turnover in 2020. Trade in nominal US dollar terms has declined more seriously than trade in volume terms. The pandemic impact on merchandise trade varied across regions.
Asia saw the smallest decline in merchandise trade, with a 0.5% decline due to coronavirus restrictions earlier than other regions, as well as good crisis management and the regions crucial role as a global supplier of consumer goods and medical devices. Meanwhile, China, the biggest exporter of goods in 2020, accounted for 13% of total world trade, up from 12% in 2019.
Among the worlds top 100 traders, Slovenia and Cambodia have risen significantly in the global merchandise trade rankings 2020, mainly thanks to their manufacturing sectors, which are well integrated into regional supply chains. In countries where commercial services mainly consists of tourism, there was a significant decline in their ranking in 2020. Examples include Macau, China and the Lebanese Republic.
Exports of goods from the least developed countries fell by 12% in 2020, while exports of commercial services declined by 35%. Goods exports have been particularly hard hit by the 30% drop in fuel prices, with fuels and mining products accounting for about half of least developed countries merchandise exports. In the services sector, these countries, like many others, have suffered from travel restrictions, as road receipts represent the largest source of revenue from service exports.
Video: https://roscongress.org/sessions/sleduyushchie-20-let/search/#02:21:57.710
Experts are optimistic about global trade recovery, which are largely dependent on the corona vaccine success.
As businesses adjusted to the new work environment and started producing vaccines in Q4 2020, trade volume recovered 1% from its pre-pandemic level in Q4 2019.
WTO economists predict strong growth in world trade, the results of which are largely dependent on GDP growth and the pandemic development. Growth in 2021 could surpass expectations if universal access to vaccines is achieved, or decline if vaccination efforts are unsuccessful.
Post-pandemic trade recovery already vary between countries and regions. Goods exports and imports in 1Q 2021 rose to new heights in Asia and returned to pre-pandemic levels in Europe and North America, but lagged behind in poorer, less industrialized regions such as Africa and the Middle East. Thus, merchandise imports increased year-on-year in all regions in 1Q 2021 except Africa (-0.9%) and the Middle East (-2.7%). The study authors note that trade recovery has been most successful in Asia and worse in regions that depend on natural resource exports.
For more information, see the special sections of the Roscongress Foundation Information and Analytical System: StayHomeEconomy and COVID-19, dedicated to possible ways to stabilize the economy during the pandemic; as well as Trade Policy, Export and Globalization / Regionalization which are dedicated to world trade.






