In a report prepared by the Spatial Development Department of the CSR in cooperation with the Center for Infrastructure Economics, a study was carried out of the boundaries of the Moscow agglomeration, including commuting, the structure of costs and features of transport behavior based on data from PJSC Sberbank, PJSC VimpelCom, Rosstat and other sources. Based on the results of the work carried out, a unique model for analyzing the territory was formed on the basis of different types of data.
The Roscongress Foundation presents the salient points of the publication accompanied by fragments of broadcasts of relevant panel discussions from the business programme of international events held by the Roscongress Foundation.
Big data shows the areas of actual spatial behavior of the population.
Modern Russian statistical accounting is carried out within the formal administrative boundaries of territories, but these boundaries do not play a decisive role in everyday life and peoples behavior. Big data makes it possible to bring territorial accounting units closer to the areas of actual spatial behavior of the population. Revealing the real boundaries of the metropolitan area and metropolis significantly increases the accuracy of analytics and forecasts of the flows of people, financial resources and information, which makes it possible to plan high-quality infrastructure for the further functional use of the territory.
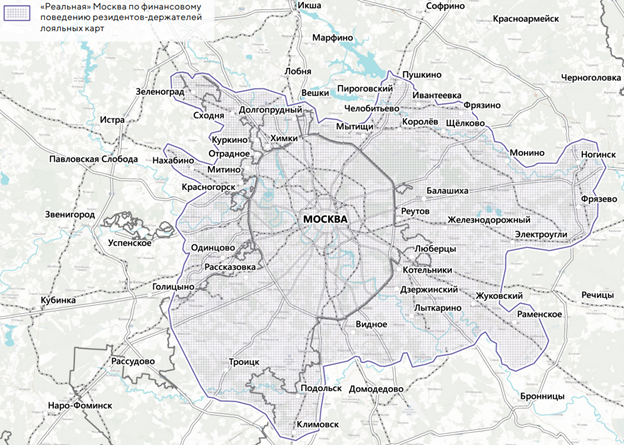
Moscows borders, measured by the financial behavior of the population, are much wider than its administrative territory.
The satellite cities adjacent to Moscow form a single labor market with the capital, acting as generators and donors of financial flows for the more distant zones of the Moscow metropolis. In addition to the Moscow region, it includes Vladimir, Ivanovo, Kaluga, Ryazan, Smolensk, Tver, Tula and Yaroslavl regions. «Real» Moscow includes the most economically developed cities of the Moscow region, such as Khimki, Mytishchi, Odintsovo. The peculiarities of the balance of financial flows make it possible to single out the functional core of the Moscow metropolis, which forms a single area of high concentration of jobs and, as a result, is the center of attraction for labor migration. The volume of outgoing financial payments exceeds the incoming ones by 20-30%, which indicates the growth of the continuous area of urbanized development. The specificity of Russia lies in the growth of the territory of a real city due to multi-storey high-rise housing, and not cottage settlements, as in the countries of Europe or North America.
Video: https://roscongress.org/sessions/umnaya-sreda-novyy-uroven-razvitiya-gorodov/search/#00:45:35.615
Moscow acts as a financial donor for the Moscow metropolis.
Moscow is the main concentration of high-paid jobs in the Moscow metropolis. More than 1/5 of the income from personal income tax to the budget of Moscow is provided by residents of other regions of the metropolis. Labor migration of the population leads to an outflow of tax revenues from the regions the amount of personal income tax not received by regional budgets is estimated at 56 billion rubles per year. However, the income of holders of bank cards opened in Moscow returns to the economy of the Moscow region and other regions of the metropolis in the form of payment for services, transfers to relatives, tourist trips, due to which there is a partial compensation for the «lost» due to labor immigration of personal income tax. The volume of such a financial «counter-flow» is estimated at about 250 billion rubles per year, which, being spent in the territory of other regions of the Moscow metropolis, can bring about 20 billion rubles of tax revenue per year. Thus, lost tax revenues are compensated by at least 35%.
Improving transport accessibility contributes to the growth of incomes of the population.
Transport accessibility can act as a decisive factor in the intensity of labor mobility and, as a result, significantly affect the incomes of residents of territories more remote from Moscow. Acceleration of passenger traffic with the main economic center acts as a factor in increasing the income of the population of the territories, allowing their residents to use the social, trade, cultural and transport infrastructure of large cities.
Video: https://roscongress.org/sessions/megapolisy-kak-faktor-ekonomicheskogo-rosta/search/#00:52:47.743
For more information, see the special sections of the Roscongress Foundation Information and Analytical System: Big Data, Location economics, Smart Cities, Infrastructure-based development, Migration, devoted to problems and technological solutions in the field of urban infrastructure development.






