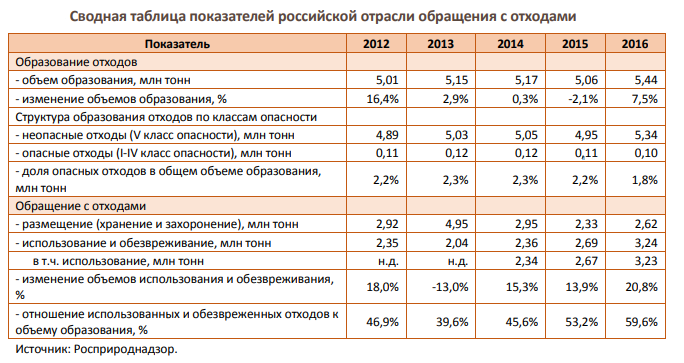
The contribution of the waste management industry to Russias GDP was 0.08% in 2016. According to the Federal Service for Supervision of Natural Resources (Rosprirodnadzor), in 2016, Russia generated 5.4 tonnes of industrial and household waste, a record high over the recent years and one and a half times more than a decade ago.
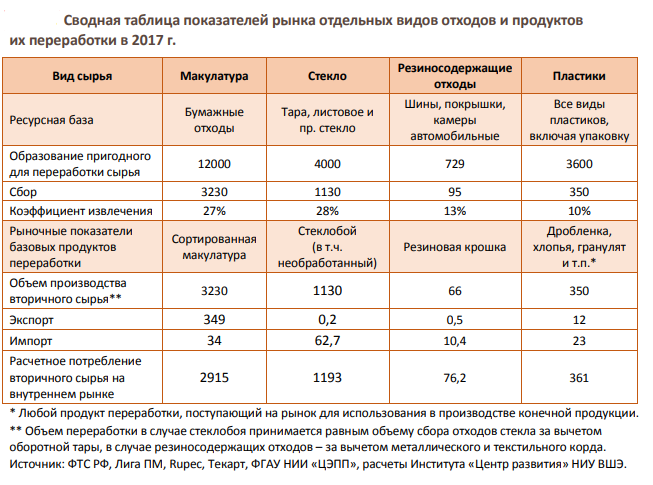
With consumption waste, the situation is fundamentally different research shows that the share of recycled waste does not exceed 10-30% here depending on how valuable the useful part of the waste is for the market. The task of analyzing the consumption waste management market is challenging because of a lack of system for collecting reliable data on waste creation and processing, so all studies are based on expert estimates and calculated values. For example, according to official data, the recycling percentage exceeds 90% for glass and 78% for used tires. Highly marketable types of waste, such as ferrous and non-ferrous scrap, are collected and recycled the most actively.
Following the global trend of environmental protection, the Russian waste management market is going through tremendous changes. Obsolete approaches to waste management are being reformed. The Government has clearly made recycling a priority, and has devised a development strategy and radically changed the legislation.
The new approach to waste management was documented in the form of legislative amendments. A landmark document is the updated version of the Federal Law No. 89-FZ «On Production and Consumption Wastes», which now includes the following: new terminology (the definition of «waste» was reformulated to make it more accurate; new concepts such as recycling, recovery, and recuperation were introduced, etc.); new principles of waste management shaping the course of the industry (priority of recycling over incineration and landfill); new regulatory mechanisms (waste disposal through landfill is now prohibited if the waste contains useful components; the scope of responsibility of manufacturers was widened; a system of regional operators was created); redefined scope of authority of regulatory agencies, etc.
The changes have laid the groundwork for a new phase of the development of the waste management industry in Russia. The waste management market is highly appealing to business due to the low base effect and prospects for growth in the consumer segment (especially so if decisions to stimulate demand for recycled products are taken at the government level). Given the stated priorities and the legislative changes, major improvements can be expected as soon as in the short term. However, this will require close collaboration between people, businesses, and the state.





